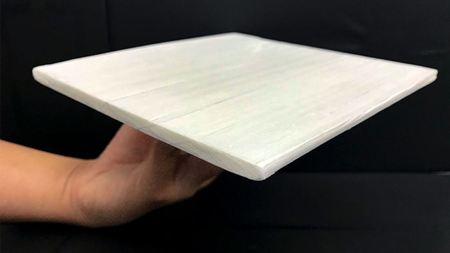
(Xinhua/TBI Africa.com) U.S. and Chinese researchers engineered a wood-based material that can reflect heat or infrared radiation and cut the energy costs of cooling buildings by up to half.
The study published on Thursday in the journal Science, reported the white “cooling wood,” highly reflective and capable of passive radiative cooling, two key properties in next-generation structural materials.
According to the study, a modeling analysis of the material in 16 U.S. cities showed that a cooling cost evaluation could be saved by between 20 per cent and 50 per cent.
Buildings account for over 40 per cent of the U.S. total energy demand and half of them is used for heating and cooling.
Passive radiative cooling materials can cool a structure by deflecting incoming solar radiation and dissipating heat energy with no energy consumption.
Researchers from University of Maryland, University of Colorado Boulder, University of California Merced and Huazhong University of Science and Technology compressed wood that has been stripped of its lignin, which are polymers making plant cells rigid.
According to the study, the process makes the wood significantly stronger and results in partially aligned cellulose nanofibers, gives the wood a highly solar reflective surface.
The cooling wood, over eight times stronger than natural wood, can dissipate heat during day and night.